Salermide
The sirtuins (SIRTs) are a family of NAD+-dependent histone deacetylases involved in gene regulation. Salermide (CAS 1105698-15-4) is an inhibitor of SIRT1 and SIRT2, causing tumor-specific apoptotic cell death. In MOLT4 leukemia cells, salermide causes 90% apoptosis within 72 hours (IC50 ~ 20 µM) by reactivating proapototic genes that are repressed by SIRT1. Salermide is a stronger Sirtuin inhibitor than sirtinol.
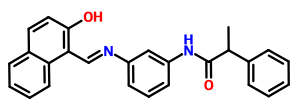
Synonyms: Salermide; (E)-N-(3-((2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)methyleneamino)phenyl)-2-phenylpropanamide
Technical Data: Molecular Weight - 394.48; Molecular formula - C26H22N2O2; CAS No - 1105698-15-4
Ordering Information: Product Number - EC-000.2468
Price and Availability: Inquire
This product is also available to buy in bulk quantities.
References:
1. Yamamoto, H., Schoonjans, K., Auwerx, J.. Sirtuin functions in health and disease. Mol Endocrinol 21(8) 1745-1755 (2007).
2. Milne, J.C., Denu, J.M.. The sirtuin family:Therapeutic targets to treat diseases of aging. Curr Opin Chem Biol 12 11-17 (2008).
Related Products: Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid; MS-275 (Entinostat); CI-994 (Tacedinaline); BML-210; M344; MGCD0103 (Mocetinostat); PXD101 (Belinostat); LBH-589 (Panobinostat); Tubastatin A; Scriptaid; NSC 3852; NCH 51; HNHA; BML-281; CBHA; Pimelic Diphenylamide; ITF2357 (Givinostat); PCI-24781; APHA Compound 8; Droxinostat; SB939.
Related service: collection of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors.